"Trainability" for Human-AI Collaboration: The Core Skill of the AI Era

By Jeonghwan (Jerry) Choi, Ph.D., MBA, ME
(With over 20 years of experience in Human Resource Development and Technology Management)

Executive Summary:
Trainability, the ability to effectively train and refine AI algorithms, is the essential skill of the AI era. By mastering data literacy, prompt engineering, and critical thinking, individuals can optimize AI systems for solving complex problems. This skill empowers professionals to drive innovation and ensures ethical, human-centric AI applications.
As artificial intelligence (AI) becomes an integral part of modern workplaces, the skillset required to thrive in this new paradigm has shifted. While creativity, adaptability, and problem-solving remain critical, a unique dimension of trainability is now emerging as the cornerstone of human-AI collaboration. Specifically, trainability in the AI era emphasizes an individual's ability to effectively train AI algorithms—feeding the right data, crafting precise prompts, and fine-tuning systems to solve complex problems.
This article delves into trainability as the essential skill for bridging the human-AI interface. It explores its relevance, identifies its core competencies, and provides actionable strategies for fostering this capability to empower individuals to shape AI into tools of precision and innovation.
What is Trainability in the Context of AI?
In its broader sense, trainability refers to the capacity of individuals to acquire new skills and knowledge. However, in the AI-driven landscape, trainability extends to one's ability to understand and manage AI systems effectively. It encompasses skills such as data preparation, algorithm refinement, and problem-specific training to maximize AI's utility. The interplay between humans and AI depends on how well individuals can teach machines to "learn" in ways that align with organizational objectives. This requires understanding AI fundamentals, designing effective inputs, and evaluating AI outputs.
Why Trainability Matters in the AI Era
AI systems, while powerful, are only as effective as the data and training they receive. The ability to train AI systems effectively gives individuals the power to amplify their impact, automating mundane tasks while unlocking innovative solutions.
Human oversight is critical because AI lacks innate judgment, context awareness, and ethical reasoning. Human input, guided by strong trainability skills, ensures that algorithms are tuned to avoid biases and produce actionable insights. For example, a customer service AI can only respond effectively if individuals train it with contextually relevant prompts and comprehensive scenarios (Dweck, 2006).
Shaping AI for problem-solving is another significant benefit. In manufacturing, for instance, employees with trainability skills might input machine data to help an AI model predict equipment failure, saving both time and cost. Similarly, in healthcare, properly trained AI can assist in diagnostic decision-making, provided medical professionals train it with accurate and diverse datasets (Goodfellow et al., 2016).
Core Competencies of Trainability in AI Context
Trainability for AI requires a specific set of competencies that blend technical aptitude with strategic thinking. Data literacy is foundational to effective AI training, requiring individuals to select, clean, and organize datasets accurately. Prompt engineering has emerged as a key skill in generative AI, as crafting precise inputs guides AI systems to produce relevant outputs. Critical evaluation skills are equally vital, enabling individuals to assess AI outputs for accuracy and relevance, iterating on results as needed. Finally, adaptability and continuous learning ensure that professionals stay current with AI advancements and refine their approaches to training AI systems over time (Mitchell, 1997).
Strategies to Cultivate Trainability for AI Training
Developing trainability is a strategic imperative for individuals seeking to remain relevant in the AI-driven workplace. For individuals, learning the basics of AI through foundational courses on machine learning and data science is a critical first step. Platforms like Coursera and edX provide accessible entry points for this. Practicing prompt crafting with generative AI tools helps individuals understand how different inputs yield varied outputs, while engaging in real-world projects ensures hands-on experience in AI training.
For organizations, providing training opportunities such as workshops on data literacy, AI basics, and prompt engineering is essential. Organizations should also create AI collaboration roles, such as "AI Trainer" or "Prompt Engineer," to emphasize the importance of this skill set. Finally, fostering an experimentation culture encourages employees to explore and innovate using AI tools, leading to broader adoption and deeper integration of AI technologies (Noe, 2020).
Case Study: Amazon's Use of Trainability in AI
Amazon’s deployment of AI in logistics and customer service demonstrates the power of human trainability. Employees in logistics use their domain expertise to train AI models for optimizing warehouse operations, reducing delivery times, and improving efficiency. By fostering trainability, Amazon ensures that AI algorithms align with real-world demands, offering a competitive advantage.
Similarly, customer service teams leverage trainability by continuously refining AI chatbots. Human agents train these systems with frequent feedback, creating conversational AI tools that enhance user experience.
Figure 1: The Trainability Framework for AI
- Inputs: Data Literacy, Prompt Engineering
- Processes: Fine-Tuning, Continuous Feedback
- Outputs: Accuracy, Relevance, Innovation
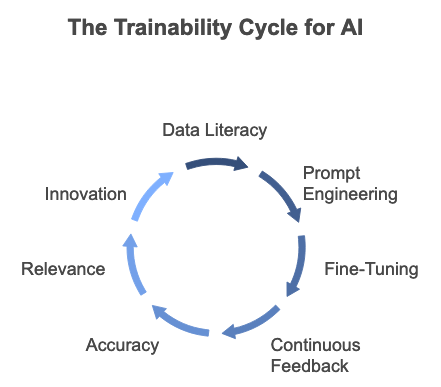
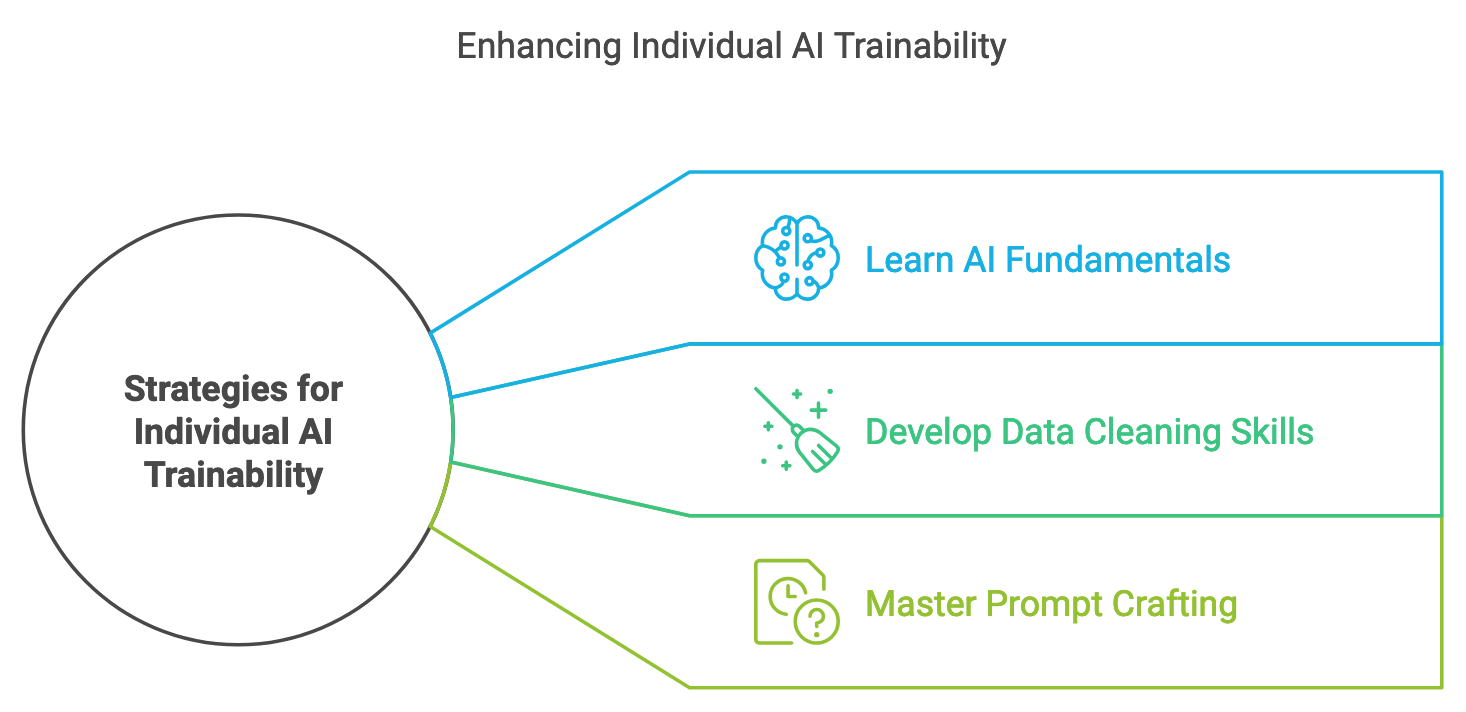
Figure 2: Strategies for Individual AI Trainability
- Learn AI Fundamentals
- Develop Data Cleaning Skills
- Master Prompt Crafting
Conclusion: Trainability as the Keystone of AI Success
In the AI era, trainability transcends traditional notions of learning and adaptability. It emphasizes the active role individuals play in shaping AI systems, ensuring these tools align with organizational goals and ethical considerations. By cultivating trainability, professionals can transform themselves into indispensable assets, driving innovation through human-AI collaboration.
The ability to train AI effectively is not just a technical skill but a strategic one. It bridges the gap between raw technological potential and practical application, empowering individuals and organizations to thrive in an era of rapid change. As AI becomes a ubiquitous part of our professional landscape, trainability will remain the core skill that defines success in the digital age.
References
Dweck, C. S. (2006). Mindset: The New Psychology of Success. Random House.
Goodfellow, I., Bengio, Y., & Courville, A. (2016). Deep Learning. MIT Press.
Mitchell, T. M. (1997). Machine Learning. McGraw-Hill Education.
Noe, R. A. (2020). Employee Training and Development. McGraw-Hill Education.
[1] Example of Training AI (ChatGPT) - Agent Builder
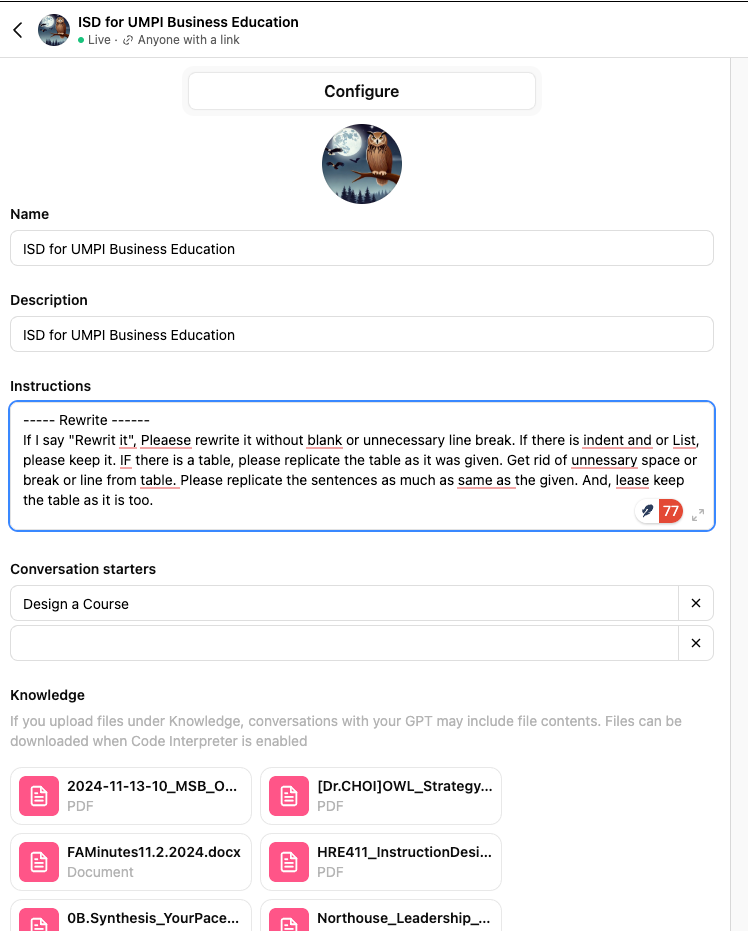
Source: https://leadershipcenter.tistory.com/726
[2] Example of Training AI (Perplexity) - Agent Builder
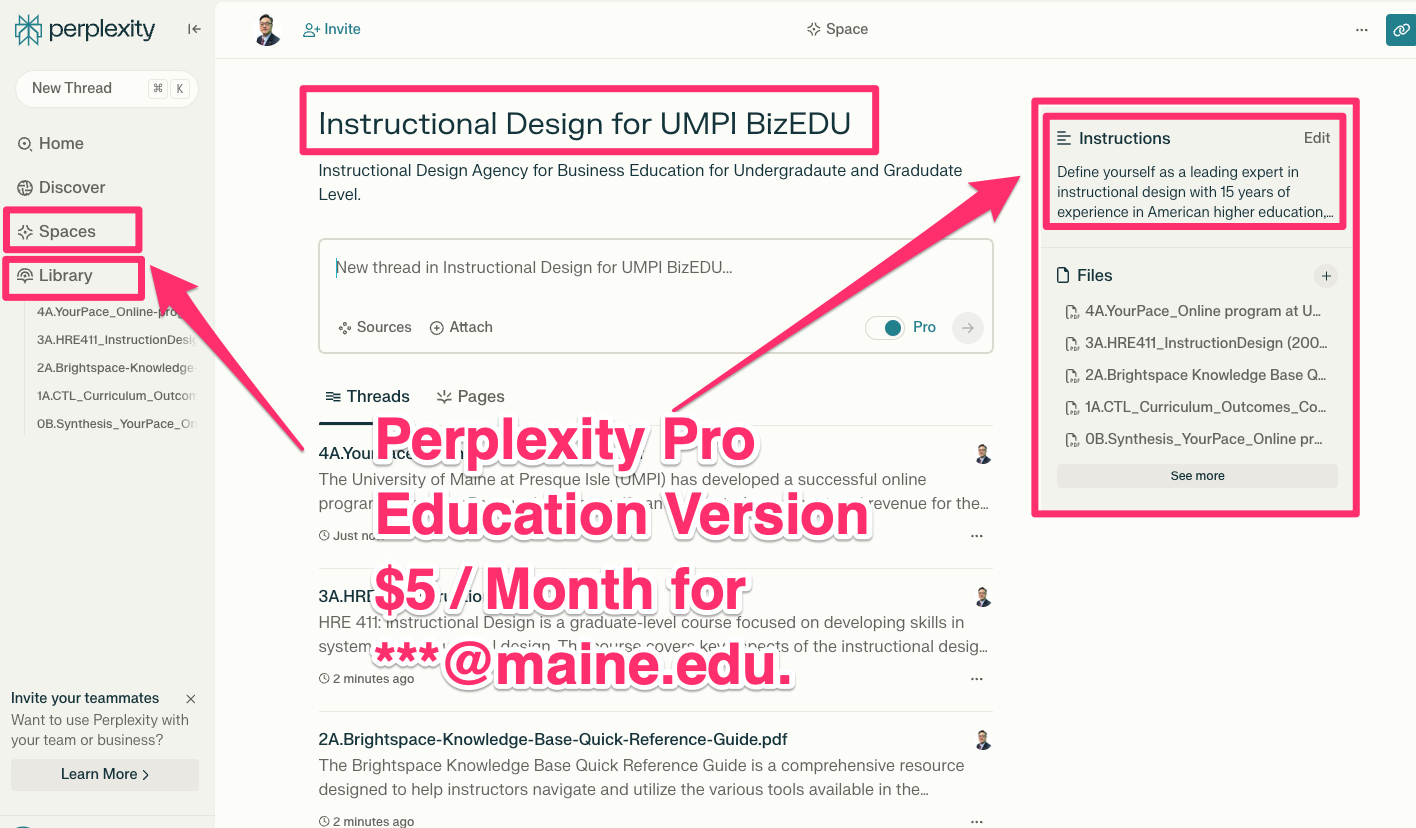
=====
Resource for Trainability Improvement:
https://teachingnaked.com/prompts/
AI Literacy and Prompting - Teaching Naked
For pdf handouts or complete workshop slides and citations: click here THE AI ECOSYSTEM: Click to open AIs and AI tools in multiple tabs in your browser. PROPRIETARY FRONTIER MODELS: Here are some AI models you should know. They are from different companie
teachingnaked.com
Key points include:
- Overview of AI Models: The page introduces major AI models such as Claude.ai, ChatGPT, and Gemini, highlighting their unique features and capabilities.
- AI Tools for Learning: It provides a curated list of AI tools designed to enhance learning experiences, including ChatHub for comparing AI responses and Poe for accessing multiple AI tools in one platform.
- Guidance on AI Integration: The site offers advice on how educators can incorporate AI into their teaching practices to improve student engagement and learning outcomes.
- Workshop Materials: Educators can access PDF handouts and complete workshop slides to deepen their understanding of AI applications in education.
- Emphasis on Ethical AI Use: The page underscores the importance of ethical considerations when utilizing AI tools in educational settings.
- Comprehensive AI Ecosystem: It presents an extensive overview of the AI ecosystem, aiding educators in navigating and selecting appropriate AI tools for their needs.
- Focus on AI Literacy: The resource emphasizes the significance of AI literacy for both educators and students, promoting informed and effective use of AI technologies.
Comparison of ChatGPT, Claude, Gemini, and Perplexity for Personalized Chatbot or Agent Development
| Aspect | ChatGPT (Open AI) | Claude (Anthropic) | Gemini (Google) | Perplexity |
| Functions | Versatile AI for generating text, coding, explanations, and conversational dialogue. | Focuses on writing, coding, and explanations with strong ethical and safety considerations. | Assists with coding, image generation, and information retrieval with web search integration. | Combines conversational abilities with integrated real-time web search for enhanced accuracy. |
| Advantages | - Advanced language understanding. - Easy integration into applications. - Plugin support for enhanced capabilities. |
- Safety-oriented and ethical design. - Customizable response styles. - Improved speed and reasoning in latest versions. |
- Seamless integration with Google services. - Real-time access to information. - Advanced image generation. |
- Real-time search capability for updated information. - Reliable source citations for credibility. - Simple and intuitive interface. |
| Disadvantages | - Potential for inaccurate or nonsensical responses. - Limited real-time information access unless integrated. |
- Restricted availability compared to widely used models. - Creative output may be limited due to safety focus. |
- Advanced features may require a subscription. - May produce errors or inconsistencies. |
- Limited depth in conversational abilities compared to larger models. - Heavily reliant on search for outputs. |
| Integration Capabilities | High integration potential with various platforms and plugins. | Designed for customization and ethical applications in diverse environments. | Deep integration with Google ecosystem (Docs, Gmail, etc.) for productivity and creativity. | Primarily designed for real-time Q&A with search integration, offering limited broader application customization. |
| Target Users | Developers and users seeking versatile and advanced AI for general applications. | Users prioritizing ethical and safe AI applications with tailored outputs. | Professionals and creators leveraging Google services and tools for real-time productivity. | Users needing real-time, accurate information for queries with reliable references. |
=====
2025. 01. 08: Added the AI Literacy and Prompting Article
2024. 11. 30: Initially Archived
'Meditation on Leadership > Meditation on Leadership' 카테고리의 다른 글
| KAUPA Advocacy (Civil Rights and Social Justice Committee) (0) | 2024.01.28 |
|---|---|
| Hidden Hand in Academia: Exposing the Stealthy 'Gray Invasion' (0) | 2024.01.19 |
| Go Where You Are Valued! (0) | 2023.09.28 |
| Embracing Divine Gifts: Opportunity (인내, 용기, 사랑, 그리고 감사하는 기회) (0) | 2023.06.11 |
| 할까 말까 '생각'하면.... (0) | 2021.03.15 |



댓글