삼성 이건희 리더십 분석
"Change everything except for your wife and children"
– Kun-Hee Lee, SAMSUNG, Chairman, Frankfurt Declaration, June 07, 1993 –
HHL-Leipzig Graduate School of Management (독일, Handelshochschule Leipzig) MBA 수업 중에 Leadership, Business, Society and Ethics...라는 수업의 Final Report로 제출한 삼성 이건희 회장에 대한 리더십 분석자료입니다.
글자수가 1500자로 제한되어 있어서 혹여 내용 중에 미흡한 것이 있을 수도 있습니다만, 나름대로 최대한 성의를 다해 객관적으로 분석해봤습니다. 다행히 리더쉽 담당 교수님이신 Manke 교수님이 좋아하셨고, 문맥을 상하지 않는 범위내에서 이 자료를 약간 수정해서 외부에 Publish 해도 되겠냐고 제안하셔서 혼쾌히 동의했습니다.
분석에도 나와있습니다만, 꿈꾸는 자, 혁신가, 실행가, 학습자 항목의 높은 평가에도 불구하고 늘 문제가 되어왔던 삼성 이건희 (전) 회장과 그 가족들의 경영 승계권을 둘러싼 비 윤리성과 인간에 대한 사랑이 적음으로 인해 사회적으로나 삼성이라는 기업집단에 크나 큰 손해를 끼쳤습니다.
물론 한 개인이 위의 분석에서 제시한 모든 조건에 완벽하게 부합하는 것은 불가능 할 겁니다. 하지만, 크게 떨어지는 조건 (이건희의 경우 도덕성과 인본주의적 사고 부족) 때문에 결국에는 크게 문제가 되었고, 결국은 회장 자리에서 내려온 채 법의 심판을 받게 되었습니다.
이렇듯 리더는 다각적이고 통합적 사고와 능력을 갖추어야 제대로된 리더십을 발휘할 수 있습니다.
윤리, 도덕이 성공을 만들어 내지는 않습니다만 이것이 없으면 혹여 짧게 성공할 수는 있어도 결국은 오래가지 못합니다.
우리가 이건희 (전) 삼성 회장과 그 일가로 부터 배우야 할 것은, 아무리 비전이 출중하고 다른 능력이 뛰어나도 확고한 윤리도덕에 바탕을 둔 인간에 대한 근본적인 사랑이 없다면 결국은 몰락하고 만다는 것입니다.
이것이 바로 노키아나 토요타 등 패밀리 들이 대기업 집단을 이끌고 있는 가족경영 기업들과 삼성 로얄 패밀리들이 결정적으로 다른 것입니다.
삼성 투자자들과 여러 Stake-Holder와 국가에서 근본적으로 삼성 로얄 패밀리들의 가치와 비용 그리고 존재이유에 대한 고민을 해 봐야 할 때가 아닌가 합니다.
* 영어로 적을 수 밖에 없었던 점은 많은 양해를 바랍니다...
한글로 번역된 "삼성 이건희 (전) 회장 리더십 분석" 은 제가 쓴 책 "교감의 리더십에 있습니다.

J.H.Choi
2008년 7월
[Retrieved on 2005 June]
Introduction
In July 2004, when Business Week published its survey of top brands in the world, Samsung, one of South Korea's best-known business groups, was 21st on the list. Samsung had also surpassed its rival, the Hyundai Group, to become the largest chaebol in South Korea. Samsung's flagship company was Samsung Electronics, the world's leading manufacturer of dynamic random-access memory (DRAM) and other memory chips, and a global player in electronic gear including LCD panels, DVD players, and cellular phones.
By the 1980s, Samsung was exporting electronics products under its own name. When Lee I died in 1987, his son Kun-Hee Lee (Lee II) assumed control (see Appendix1). In 1990, after years of importing technology and spending heavily on R&D, Samsung became a world leader in chip production. In 1993, Lee declared “SAMSUNG New Management” at Frankfurt. This declaration is the first step to be a “Global Leader” in IT industry.
In this article, by using the leadership principles which have been introduced by lecturers in LBES classes, Lee’s leadership is presented and analyzed.
Principles of Leadership
Many researchers introduced various “Leadership Principles” and also many practitioners such as GE, HP, AT&T developed specific principles and applied them in practice. HHL’s Leadership and Business Ethics and Society classes provided theoretical and practical approach for addressing principles of leadership. Each class had unique lecturers who emphasized different leadership principles. These leadership principles are presented as Appendix 2. The principles are: Be a Dreamer, Be a Learner, Be a Humanist, Be a Futurist, Be a Planner, Be a Doer, Keep Principles, and Be an Innovator.
Be a Dreamer
In the Genesis, Joseph story tells us the importance of being a dreamer as a leader. Having a dream is quite important to be an effective leader. Vision or mission is the realization of dreams. Making a clear goal is one of the essential management skill .
When Lee II took over Samsung as a Chairman on 1987, the group was recognized in the global arena as just a mid-tier vendor of me-too products and was no match for SONY. Lee II dreamed to overcome this situation and started changing Samsung as a global leader in IT industry.
Be a Learner
Dr. Saalbach said “My attitude determines my altitude” which were emphasizing the importance of open-minded attitude for learning from others.
In 1990, after years of importing technology and spending heavily on R&D, Samsung became a world leader in chip production. Encouraged by the Lee II, Samsung agreed to cooperate with another chaebol Goldstar (which became the LG Group) to obtain foreign technology to develop liquid crystal displays. He did not hesitate to learn from others even if it hurt the pride of Samsung. A few years later, LCD division became a one of biggest cash cow.
Be a Humanist
Dr. Suchanek pointed out the one-sided Friedman’s explaining for Corporate Social Responsibility . Maximizing Profit is not enough to guarantee the sustainability of society. He suggested the integrity approach, maintaining the license to operate, to explain the conflict between moral to profit. To secure the license to operate, corporate should invest tangible and intangible resources.
Samsung has invested lots of not only tangible assets (1.07bil. $ - 29% of profit, invested to the community activities) on 2001 but also intangible assets such as social welfare program, environmental preservation and cultural and arts programs to take corporate social responsibility.
On the other hand, Lee II has been criticized for keeping “No labor union” policy and transferring his throne to his son. These controversial unethical actions undermine the real value of Samsung.
Be a Planner
Sensing and planning for the future is very critical to a leader. Lee II had a good sense of changing Samsung from bureaucratic organization to fast moving one during 1990’s. But, he failed to anticipate the paradigm shift in automotive industry. From the first step in 1994 to the first car rolled off the assembly line in 1998, Samsung Auto suffered operating losses and crushing interest charges. Within a few years, Samsung was forced to divest the car business for a fraction of its initial investment.
Be a Doer
Everybody can make a plan but only few people can do it. When Lee II declared the “New management” at Frankfurt, He started his presentation at 8 p.m. stressing the pressing need to reinvent the group via bold changes and quality management and the event continued nonstop for about seven hours. Since then, Lee II himself had spearheaded the group-wide efforts to shift its focus from sales and quantity to quality, setting defective products as enemy No.1. When he did change the culture, he used “Empowerment” to employees.
Be an Innovator
In 2001, Dr. Hwang, CEO of Samsung Electronics, should decide the type of Flash memory. NOR type was quite popular in the market, but Lee II ordered changing it to NAND type. He also refused the joint-venture offer from TOSHIBA, which means he should take all risks to innovate the memory industry standard.
Now Samsung’s NAND Flash Memory is the dominant memory chip of Mobile Digital Appliances in the world.
Measures of Leadership
Kosestenbau suggested the Leadership Diamond model , and Kouzes and Posner measured the characteristics of admired leaders . In this article, six leadership principles are presented and applied at Kun-Hee Lee to measure his leadership effectiveness.
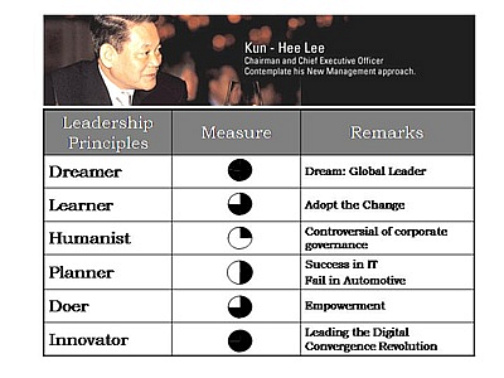
Figure: Leadership Measures of Kun-Hee Lee
In the figure, Lee II is a good “Dreamer” and “Innovator” but his relatively Low Humanist principle (i.e. aggressive attitude to stake-holders) undermines the effectiveness of his strong leadership.
Conclusion
In LBES classes, theoretical and practical leadership practices were presented by lecturers. Six leadership principles were extracted and applied at Kun-Hee Lee, Chairman of Saumsung to analyze his leadership. Lee II is a good dreamer and innovator, which makes a great success in IT industry. But his not be a good humanist makes him be challenged from society.
The leadership principles which were lectured in LBES classes should be kept in mind for every young talent who hope to be a great leader in his/her future career.
References:
1. Peter Drucker, “What Makes an Effective Executive,” HBR June 2004
2. Jim Collins et al, “Built to last: Successful Habits of Visionary Companies”, Wharton Forum, 1996
3. Slater, “The GE Way”, Fieldbook, 2000
4. S.J. Lee, “HP Competencies Model”, Strategic Leadership, 2005
5. Takao Kato, “The Productivity Effects of Participatory Employment Practices: Evidence from New Japanese Panel”, Industrial Relations, Oct. 2002
6. Andreas Suchanek, “Is Profit Maximization the Social Responsibility of Business?”, Pies, M. Leschke (eds.,2004)
7. www.samsung.com – Community Relations
8. Montly Joongang, “Interview with Dr. Hwang, CEO of Samsung Electronics”, Nov. 2004
9. Koestenbaum, “Leadership-The Inner Side of Greatness”, Jossey-Bass, 2002
10. Kouzes and posner, The Leadership Challenges, 2002
'Frequently Viewed Articles' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 법륜 스님의 남북통일에 대한 직문직답 그리고, 통일 첫 세대 육성을 위한 제언. (0) | 2010.09.26 |
|---|---|
| [반론] 대학교육보다 기업교육이 더 문제다. (6) | 2010.07.30 |
| 인재가 있으되 쓰지 못하고, 오히려 죽였던 세상 (Abandoned Talents) (2) | 2010.06.28 |
| 이명박 대통령 리더십 위기는 필연이다. (6) | 2008.07.22 |
| 백두산 여행기 그리고 하늘함 도인 이야기 (0) | 2008.07.13 |



댓글